Question
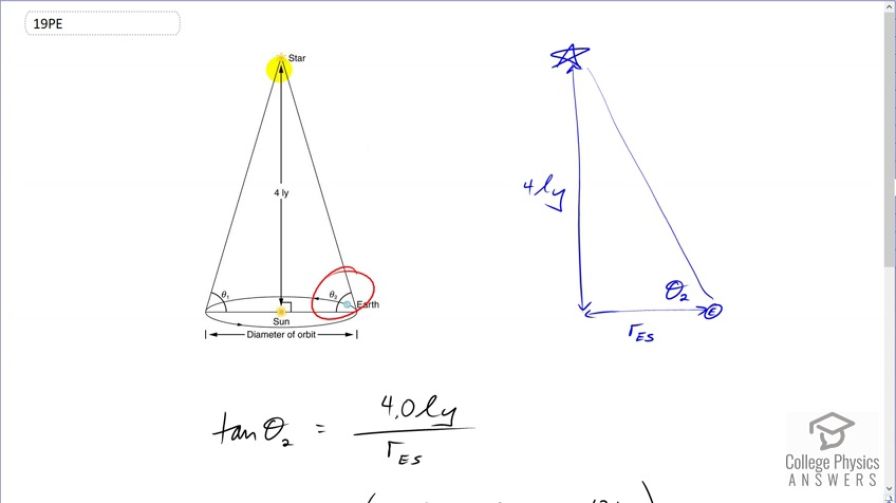
Distances to the nearest stars (up to 500 ly away) can be measured by a technique called parallax, as shown in Figure 34.26. What are the angles and relative to the plane of the Earth's orbit for a star 4.0 ly directly above the Sun?
Final Answer
or if one has 7 significant figures in the measurements.
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics, Chapter 34, Problem 19 (Problems & Exercises)
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Calculator Screenshots
Video Transcript
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. We are going to measure this parallax angle between the Earth and this distant star which is 4 light years directly above the Sun and we can draw this triangle here where this leg is 4 light years; this leg is the Earth-Sun distance and this Θ 2 is the angle we want to find. Now the tangent of Θ 2 is going to be the opposite, which is 4 light years, divided by the adjacent which is the Earth-Sun distance and we can find the angle by taking the inverse tangent of both sides. So the angle is the inverse tangent of four light years converted into kilometers divided by the Earth-Sun distance in kilometers giving essentially 90 degrees to two significant figures or 89.99977 degrees.
