Question
(a) How much heat transfer is necessary to raise the temperature of a 0.200-kg piece of ice from to , including the energy needed for phase changes? (b) How much time is required for each stage, assuming a constant 20.0 kJ/s rate of heat transfer? (c) Make a graph of temperature versus time for this process.
Final Answer
- please see the graph in the solution video.
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics for AP® Courses, Chapter 14, Problem 17 (Problems & Exercises)
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Calculator Screenshots
Video Transcript
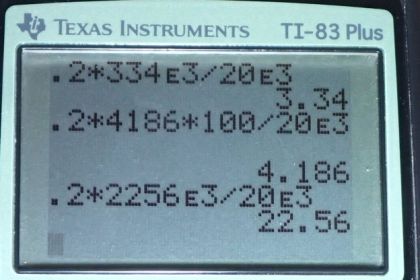
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. In this question we are going to raise the temperature of ice which is at negative 20 degree Celsius initially to final temperature of 130 degrees Celsius and which point it will be steamed and the mass is 0.2 kilograms and we have to account for whole bunch of different stages in this process. So, the first amount of energy is the amount of energy required to due to the first change of temperature the first delta T one and that’s to get from negative 20 degree Celsius to zero and then there is the heat due to the latent heat of fusion. This is the heat required to change the phase from solid to liquid and well at constant temperature of the zero degree Celsius and then we have the amount of energy needed to change the temperature from delta T two from zero degree Celsius up to 100 degree Celsius and then at 100 degree Celsius there is another phase change from liquid into vapour and so we have this heat required for that and then after its all turned into vapour there is another change in temperature we called it delta T three which goes from 100 degree Celsius to 130 degree Celsius. Let’s substitute for these terms now with some more variables. So, we have heat for delta T one is the mass times the specific heat of ice times delta T one and then add to that mass times latent heat of fusion for phase change first one from solid to liquid and then add to that the mass times specific eat of water times delta T two and notice that specific heat of water and specific heat of ice is different means it’s the same chemical substance H two O but the different phases causes different specific heat and so this delta T two is gonna be between zero and 100 and then we have the heat for vaporization mass times latent heat of vaporization and then add to that the energy needed to change the temperature of steam from 100 to 130 degree Celsius. So, mass is the common factor that we can factor out and re write it like this. Now delta T one is from final temperature zero minus the initial temperature negative 20 for a change in temperature of 20. delta T two is 100 degree Celsius and delta T three is from 130 to 133……. To 130 from 100 and that’s 30 Celsius degrees. Ok and then we plug in numbers and so that’s 0.2 kilogram multiplied by specific heat of ice times delta T one plus the latent heat of fusion for ice and then add to that the specific heat of water times 100 Celsius degrees that’s delta T two and then add to that the latent heat of vaporization for water and then add to that the specific heat of steam multiplied by the temperature change of 30 Celsius degrees there and this case the total energy of 6.19 time ten to the five joules. Ok. So, the next question is how long does each portion take… how do they word that… how much time is required for each stage? Ok. Assuming 20 kilowatts of power. So, poer is the amount of energy divide by time and then we solve for time by multiplying both sides by T divided by P and we have on left T on the right Q over P and so T one will be the heat required to change the temperature from negative 20 to zero divided that by the power. So, its 0.2-kilogram times specific heat of ice times 20 Celsius degrees divided by the power 20 kilowatts is basically what that is and that’s workout to 0.418 seconds not pretty much time. Time two which is the amount of time to melt the ice and change its phase from zero to… from solid to liquid while at zero degree Celsius is 0.2 kilograms times latent heat of fusion for ice divided by the power which is 3.34 seconds and then time three is for changing the temperature from zero to 100 and so we multiply that change in temperature by the specific heat of water and then multiply them by the mass and then divided by the power and that’s 4.19 seconds and then the time required to boil it away after its temperature is 100 and its gonna be 0.2 kilogram times latent heat of vaporization and then we divided by the power and that’s 22.6 seconds and then we have finally the time it take to change the temperature from 100 to 130 degree Celsius which is 0.456 seconds. So, that total time is 31.0 seconds after you add up each stage and lastly and part c we have a graph of temperature vs time and so the first 0.418 seconds we go from negative 20 up to zero degree Celsius and then we pause there for little while as the phase change from solid to liquid is occurring and then at this point which is 3.34 plus 0.418 we start to increase the temperature and we do this for duration of 4.19 seconds until we get here and which point we are waiting for 22.6 seconds for the phase change from liquid to vapour to occur and then… then after it finds the all vapour the temperature increases in a short period of time of 0.456 seconds from 100 to 130 degree Celsius.