Question
What is the kinetic energy in MeV of a -meson that lives as measured in the laboratory, and when at rest relative to an observer, given that its rest energy is 135 MeV?
Final Answer
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics for AP® Courses, Chapter 28, Problem 57 (Problems & Exercises)
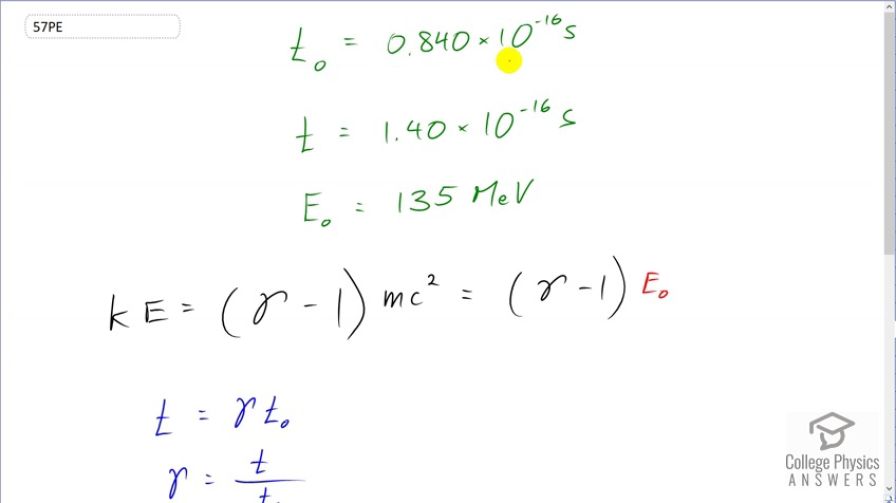
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Calculator Screenshots
Video Transcript
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. The lifetime of the Pi meson, when measured at rest, is going to be the proper time. So that's 0.840 times 10 to the minus 16 seconds, we are told. And then when the Pi meson is moving, it's going to be relativistic time which will be greater since time dilation means dilation means bigger and so this lifetime would be bigger as a result of the Pi meson moving and then it'll be 1.40 times 10 to the minus 16 seconds. And we are told that the rest energy of the Pi meson is 135 megaelectron volts and we need to figure out, what the kinetic energy of it is? So the kinetic energy is the Lorentz factor minus 1 times mc squared. And mc squared is another expression for rest energy—E naught. And so we can substitute that, which we know, 135 megaelectron volts. Then we want to create an expression for gamma and we know that relativistic time is the Lorentz factor multiplied by proper time. And so we'll solve for gamma by dividing both sides by T naught and we get gamma is t over t naught and both of these things are given to us in the question. So we substitute t over t naught in place of gamma, in our formula for kinetic energy. So kinetic energy then is t over t naught minus 1 times the rest energy. And that is 1.40 times 10 to the minus 16 seconds divided by 0.840 times 10 to the minus 16 seconds minus 1 times 135 megaelecton volts giving a kinetic energy of 90.0 megaelectron volts.
