Question
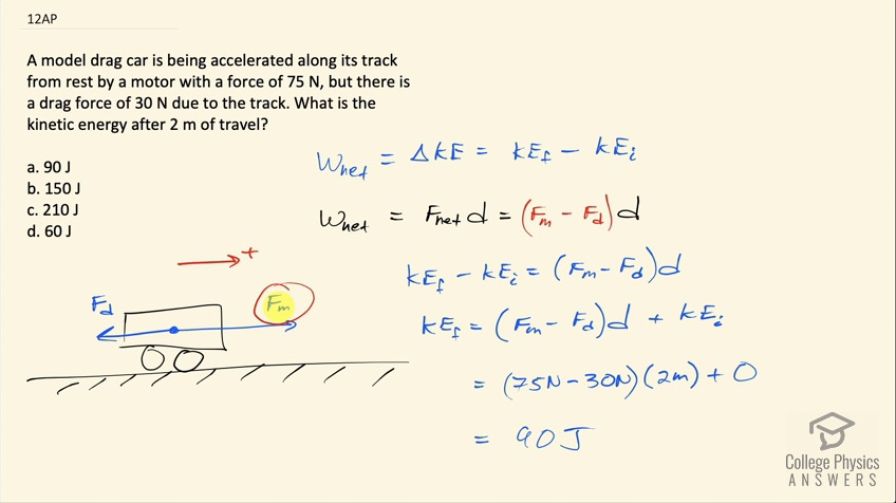
A model drag car is being accelerated along its track from rest by a motor with a force of 75 N, but there is a drag force of 30 N due to the track. What is the kinetic energy after 2 m of travel?
- 90 J
- 150 J
- 210 J
- 60 J
Final Answer
(a)
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics for AP® Courses, Chapter 7, Problem 12 (Test Prep for AP® Courses)
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Calculator Screenshots
Video Transcript
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. A model car is being accelerated horizontally along a track by a motor and so there's some force subscript m for 'motor' applied to the right say and the right is the positive direction; then there's also a drag force in the opposite direction to its motion going to the left and what is the kinetic energy after it travels 2 meters is the question? So the net work done on the car is its change in kinetic energy which is the final kinetic energy minus the initial kinetic energy and we can also say the net work done is the net force multiplied by the displacement and the net force is the force due to the motor to the right minus the force due to drag to the left and then we multiply that by d. So if both of these things are equal to the net work that means they are equal to each other and that's what we write here and we solve for final kinetic energy by adding initial kinetic energy to both sides although that initial kinetic energy is zero so it doesn't really matter but anyway here's an expression for final kinetic energy. So that's going to be 75 newtons— due to the motor— minus 30 newtons—due to the drag— all multiplied by 2 meters plus 0 kinetic energy to start with and the final kinetic energy will be 90 joules so the answer is (a).
