Question
Suppose that the average velocity, , of carbon dioxide molecules (molecular mass is equal to 44.0 g/mol) in a flame is found to be . What temperature does this represent?
Final Answer
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics, Chapter 13, Problem 45 (Problems & Exercises)
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Calculator Screenshots
Video Transcript
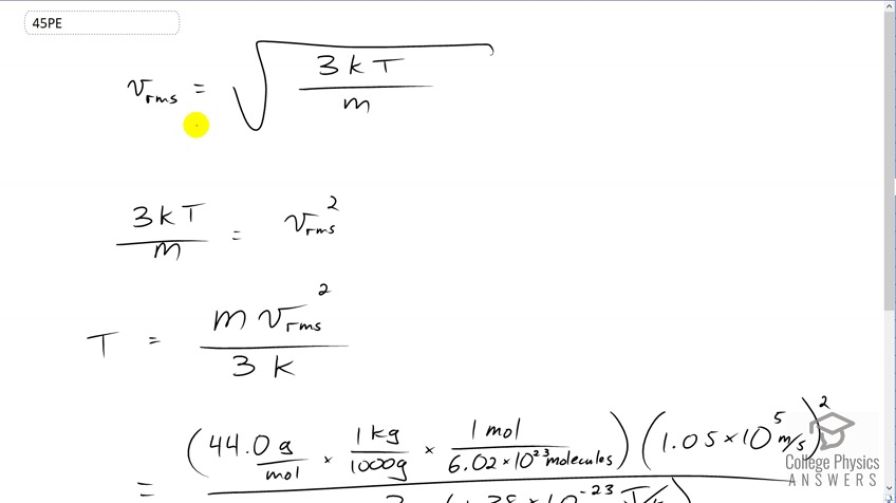
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. We're given the root mean squared average velocity of carbon dioxide molecules in a flame and we have to figure out what the temperature of that flame must be. So we know that v rms equals the square root of three times Boltzmann's constant times the absolute temperature divided by the mass per molecule. So we'll square both sides and switch the sides around. We get three k T over m equalsv rms squared. So we squared both sides there. Then we solve for T by multiplying both sides by m over three k. Then we have temperature is mass times v rms squared over three times Boltzmann's constant. So the mass is 44.0 grams per mole and we have to convert this into kilograms per molecule because most of our formulas expect MKS units, meters, kilograms, seconds. So multiply by one kilogram for every one thousand grams and then multiply by one mole for every 6.02 times ten to the twenty-three molecules, this is Avogadro's number, and then we multiply by the speed that we're told is 1.05 times ten to the five meters per second. Then we square that and divide by three times Boltzmann's constant and we get 1.95 times ten to the seven Kelvin must be the temperature of the flame.
