Question
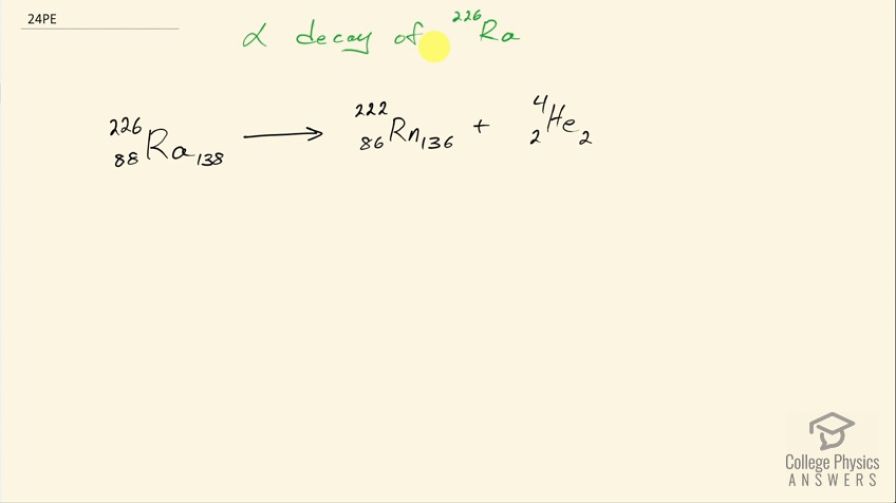
Write the complete decay equation for the given nuclide in the complete notation: decay of , another isotope in the decay series of , first recognized as a new element by the Curies, poses special problems because its daughter is a radioactive noble gas.
Final Answer
Please see the solution video.
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics for AP® Courses, Chapter 31, Problem 24 (Problems & Exercises)
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Video Transcript
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. The alpha decay of radium turns it into radon so when we look up in the appendix what the atomic number is of radium—226— we can see that it is 88 so it has 88 protons and so we write radium with a 226 up here for the total number of nucleons and then 88 is the number of protons since that's what the appendix at the end of the textbook says and 138 is 226 minus 88 the number of neutrons that are in this nucleus. So this turns into a different element plus a helium nucleus so an alpha particle is a helium nucleus that has 2 protons and 2 neutrons for a total of 4 nucleons and since there are 2 protons lost, we look up in the appendix to see which element has an atomic number of 86 and that is radon. So radon is produced and it has 2 fewer neutrons as well and radon is a radioactive noble gas and it's something that people who live in certain parts of the world have to test for in their homes because it can leach in through radioactive decay occurring in the ground underneath the home.