Question
Write the complete decay equation for the given nuclide in the complete notation. Refer to the periodic table for values of Z:
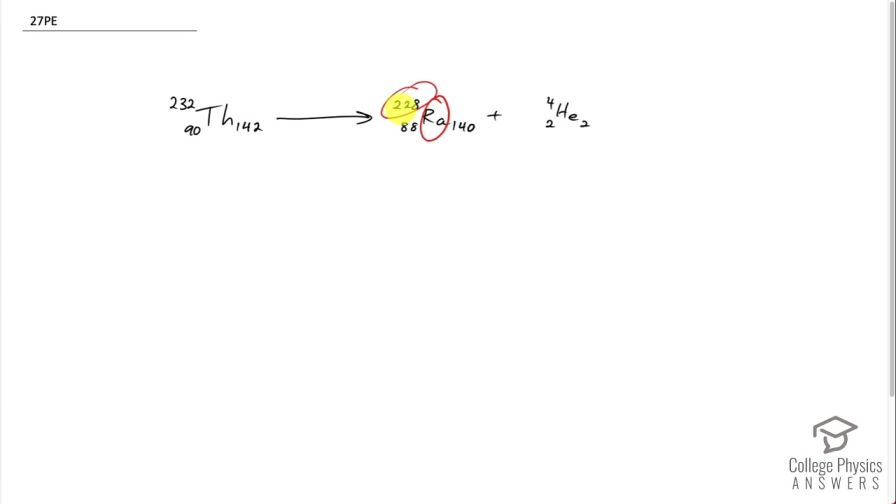
decay producing . The parent nuclide is nearly 100% of the natural element and is found in gas lantern mantles and in metal alloys used in jets ( is also radioactive).
decay producing . The parent nuclide is nearly 100% of the natural element and is found in gas lantern mantles and in metal alloys used in jets ( is also radioactive).
Final Answer
Please see the solution video.
Solution video
OpenStax College Physics for AP® Courses, Chapter 31, Problem 27 (Problems & Exercises)
vote with a rating of
votes with an average rating of
.
Video Transcript
This is College Physics Answers with Shaun Dychko. This question tells us that radium with an atomic mass of 228 undergoes alpha decay. So alpha decay produces an alpha particle, which has 2 protons and 2 neutrons with a mass number of 4, in other words and we have to look up in the periodic table of elements or appendix [A] of the textbook to figure out what the atomic number of radium is and it turns out to be 88 so we can write down 88 here; the question gives us 228 as the mass number and 228 minus 88 is 140 neutrons and with alpha decay, we know that the parent nuclide will have a number of protons equal to the sum of the radium and the alpha particle so 88 plus 2 making 90 and we can look up in the appendix [A] which element has an atomic number of 90? And that is thorium. And we know that there are 2 neutrons to add to the neutrons in the radium for a total of 142 for thorium and the mass number then is 142 plus 90, which is 232 and we are done here... we see that the number of nucleons is conserved— as it has to be— 232 on the left is the total of 228 plus 4 on the right side and charge is conserved and so on. There we go!